Back pain can be relentless—but what if the solution isn’t just rest or medication? Many wonder what Pain Management does for back pain, yet few truly grasp its full impact. Could it be doing more behind the scenes than you realize? Before you accept discomfort as your new normal, you’ll want to see what’s really at play…
Learn about pain management in the Bronx for back pain relief!
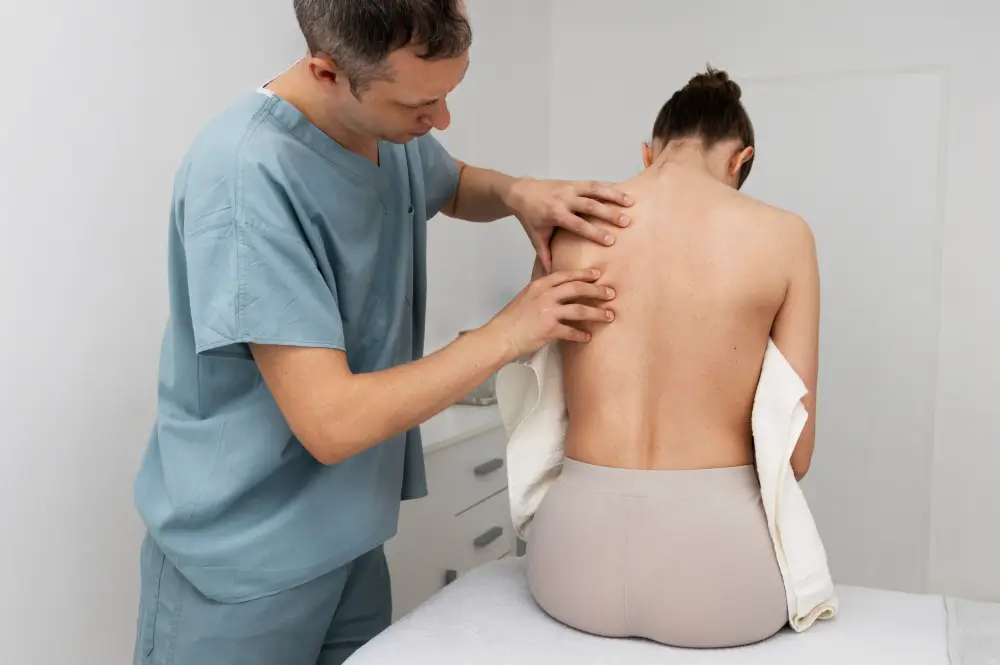
How does pain management address back pain specifically?
Back pain treatment focuses on relieving discomfort and improving function through a combination of personalized approaches. Over 80% of people experience back pain, often due to common causes like disc degeneration, joint arthritis, or ligament sprains.
Pinpointing the exact cause can be difficult, as there may not be a clearly identifiable structure responsible. If pain lasts longer than three months, discussing diagnostic options with a healthcare provider is recommended.
Treatment typically includes physical therapies, mental strategies, and nutritional approaches. Healthy cognitive practices like meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, or pain reprocessing help reduce the emotional toll of pain and support recovery.
Regular exercise adds to this by strengthening muscles and improving endurance. Functional training, yoga, low-impact cardio, or foam roller stretches can be effective when practiced consistently. Some initial muscle soreness may occur, but gradually resuming activity helps improve tolerance over time without worsening the condition.
Reducing inflammation is also essential, as it can be a significant cause of pain. Dietary changes may help manage inflammation. Together, these interventions address back discomfort holistically, helping patients regain quality of life and return to the activities they enjoy.
Diagnosis of Back Pain
The first step in diagnosing back pain involves a detailed medical history and a thorough physical exam. During this stage, the provider asks about pain duration, intensity, location, and other related symptoms like weakness, numbness, or tingling.
The physical exam assesses the spine, mobility, and any signs of nerve compression. This initial evaluation helps guide further testing and treatment planning.
Depending on clinical findings, additional studies may be ordered:
- Imaging Tests: Used to visualize internal structures of the spine and surrounding tissues.
- Blood Tests: Helpful when infection or systemic inflammation is suspected.
- Nerve Studies: Electromyography may be used to assess nerve and muscle activity and detect injuries or compression.
This step-by-step approach treats back pain accurately and effectively, favoring noninvasive options before considering more aggressive treatments.
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy and personalized exercises are essential components of back pain management, whether acute or chronic. These strategies relieve pain, improve mobility, strengthen back muscles, and support better posture and injury prevention.
Professional guidance helps tailor treatment to each patient’s specific needs.
Physical Therapy for Back Pain
Therapeutic techniques are designed to target different aspects of pain:
| Manual therapy | Releases muscle tension, improves mobility, posture |
| Heat and cold therapy | Heat relaxes muscles, cold reduces inflammation |
| Electrical stimulation | Temporarily blocks pain signals |
| Stretching exercises | Boost flexibility and ease stiffness |
| Strengthening exercises | Stabilize the spine and prevent recurrence |
| Traction therapy | Reduces pressure on spinal discs |
| Education and guidance | Promotes safe posture and movement habits |
These methods are used strategically based on the pain’s intensity and the patient’s physical capabilities.
Exercises for Back Pain
Exercise types vary in focus but all support recovery:
Flexibility Exercises
- Cat-cow stretch
- Bridge pose
- Knee-to-chest stretch
Strengthening Exercises
- Controlled crunches
- Planks
- Back muscle engagement
Balance Exercises
- Single-leg balance
- Core-focused movements
Walking and Aerobic Activity
Regular physical activity like walking or low-impact cardio improves circulation, boosts energy, and supports overall well-being, helping reduce back pain.
By integrating physical therapy and exercise into a back pain plan, both symptoms and root causes are addressed. This helps promote effective recovery and empowers patients to prevent future pain through movement, strength-building, and posture awareness.
Pain Medications
Back pain treatment may involve different types of pain relievers depending on intensity:
| Medication Type | Examples | Main Use |
| Simple analgesics | Acetaminophen | Mild pain |
| NSAIDs | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Pain with inflammation |
| Opioids | Hydrocodone, Oxycodone | Severe pain, controlled use |
Back pain management involves accurate diagnosis, physical therapy, custom exercises, and, when needed, responsible medication use. A well-rounded plan led by professionals can relieve discomfort, improve mobility, and help prevent recurrence.
Nerve Blocks or Injections
Nerve blocks and injections are procedures used to ease back pain and spine-related issues. Their main goal is to reduce inflammation and block pain signals, offering temporary but significant relief to improve function.
Each type serves a specific purpose based on the pain’s location and source:
| Type of Block | Location/Application | Primary Purpose |
| Epidural injections | Around the spinal cord (epidural space) | Reduce inflammation, ease pain |
| Intrathecal injections | In spinal fluid area | Directly block pain signals |
| Nerve blocks | Around specific nerves | Interrupt pain transmission |
| Sciatic nerve block | Lower back into leg | Relieve radiating sciatic pain |
| Celiac plexus block | Abdomen/upper body area | Target pain in those regions |
These procedures are useful when pain limits progress with less intensive treatments and must always be performed under medical supervision.
Stress Management and Psychological Therapies
Stress management and psychological therapies play a supportive role in treating back pain. These approaches reduce the perception of discomfort and support physical and emotional function.
Psychological techniques like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy help shift negative thinking patterns related to pain, improving how patients respond to their condition. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy teaches patients to live with pain while focusing on values and goals. Practices like mindfulness help individuals stay present and acknowledge emotions without judgment, reducing anxiety and building resilience.
Together, these psychological and stress-related strategies offer a broader approach to back pain care. They address not only physical factors but also emotional and behavioral ones, helping patients regain control and improve day-to-day well-being.
Sources:
- Anand, P., Dickenson, A., Finco, G., Marinangeli, F., Polati, E., Romualdi, P., … & Canonico, P. L. (2019). Novel insights on the management of pain: highlights from the ‘Science of Relief’meeting.
- Mehta, S. S., Ayers, E. R., & Reid, M. C. (2018). Effective Approaches for Pain Relief. Effective Treatments for Pain in the Older Patient, 1.


