Skin infections may occur due to several reasons. They can be fungal, bacterial, parasitic, or viral. Additionally, they can be both non-contagious and contagious. Their symptoms vary significantly, which makes management and treatment different for various skin infections. This write-up compares the two most common categories of skin infections: bacterial and fungal.
About Bacterial Skin Infections
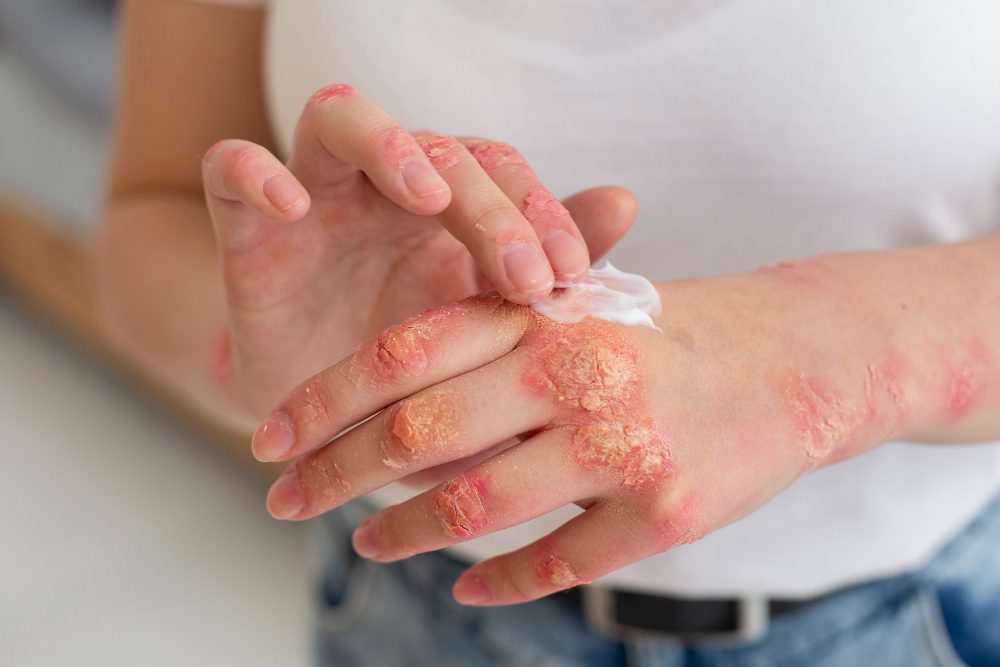
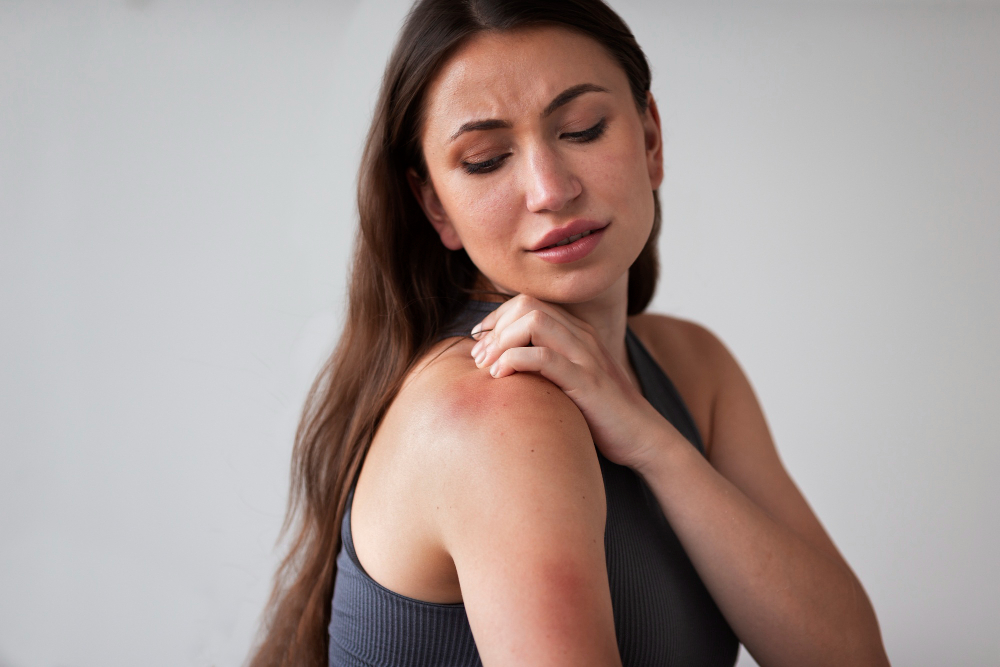
These infections occur when your skin gets exposed to bacteria. Bacteria enter human skin typically through wounds and hair follicles. Common examples of bacterial skin infections are:
- Folliculitis
- Cellulitis
- Impetigo
There are more severe forms of bacterial infections affecting the skin, such as Lyme disease, which is caused by the Borrelia bacteria. It begins with the skin but later (when not treated) progresses to the patient’s joints, brain, and heart. This makes prompt diagnosis and treatment of bacterial skin infections mandatory. If you have any red, painful, and swollen areas on your skin, visit your general physician (GP) for a correct diagnosis.
How to Identify Bacterial Skin Infections?
- The common indicator of bacterial skin infections is inflammation. Inflammation often causes swelling, redness, and heat generation in the affected skin.
- Pus formation is also common in this type of skin disorder. It is typically a thick, white, or yellow discharge containing dead skin tissue, dead bacteria, and WBC. These symptoms are more common in infections like boils, cellulitis, and impetigo.
- Like all bacterial infections, bacterial skin infections also spread easily. Spreading is more common when the infected area gets scratched, and a healthy individual’s skin gets exposed to it. Maintaining hygiene is the only way to prevent such events.
- The skin symptoms may occur with other physical symptoms like extreme fatigue, muscle aches, and headaches.
- When not treated at the right time, the skin infection can cause fever and chills. One may also get swollen lymph nodes.
Bacterial Skin Infections Treatment
Visiting a GP is crucial for the proper management of these infections. You should never administer over-the-counter medications assuming it’s a bacterial infection. Let the doctor diagnose the problem and prescribe the right antibiotics. Depending on the seriousness and types of symptoms, your doctor may prescribe oral or topical antibiotics. Your job will be taking care of the wound following the doctor’s instructions. This may include cleaning the area, applying dressings, applying medications, completing the full course of the oral antibiotic, etc.
If the wound is on one of your limbs, keeping it elevated will help you avoid swelling and maintain blood flow. This will speed up healing. Never pick or touch the affected skin. It will not only hinder the healing process but will also cause the spread of the bacteria.
About Fungal Skin Infections

You get fungal skin infections when fungi grow inside or on your skin. Fungal infections mostly cause red, scaly rashes on the affected area. Extreme itchiness in the infection area is a common indicator of fungal infection. When things get worse, you may also have a burning sensation. The most common fungal skin infections are:
- Candidiasis, which is caused by the Candida fungus
- Fungal infections caused by Dermatophytes (examples include athlete’s foot, jock itch, etc.)
Other than these, you may develop fungal skin infections from mold and yeast. As fungi need damp, warm environments to grow, they are more common in skin folds, the groin area, and feet.
How to Identify Fungal Skin Infections?
- Severe itching is one sign that separates fungal skin infections from their bacterial counterpart. Itchiness is usually constant and even impairs normal living.
- If you see your skin become dry, flaky, and scaly, you most likely have a fungal infection.
- When fungal infections affect the nails, they cause thickening and discoloration. Additionally, your nail may become brittle and come out of the nail bed.
Fungal Skin Infections Treatment
Like bacterial skin infections, fungal skin infections are also treated with oral or topical medications. Your GP may also advise you to use a combination. Ointments formulated for topical applications typically contain Miconazole, Clotrimazole, Terbinafine, or Ketoconazole. These ingredients are also present in shampoos prescribed for fungal infections on the scalp. The usual duration for which one should use the antifungal ointments/shampoos is two to four weeks, or as advised by your doctor.
Doctors always prescribe medications to manage severe symptoms of fungal skin infections. The drugs they use for this purpose include Itraconazole, Fluconazole, and Terbinafine. The doses typically continue for two to 12 weeks. If it’s an infection of the nails, the doses tend to be longer. Irrespective of the kind of infection you have on your skin, contact Magnet Health NY for the right advice. The clinic has the best physicians who will quickly diagnose the actual cause of the problem and prescribe medications. You will experience complete remission much faster if you rely on Magnet Health.


